+86 13816508465
Pump Knowledge
Nov. 17, 2025
Maintaining consistent water pressure in modern buildings is a fundamental challenge. For residents, it means a reliable shower and functional appliances. For commercial and industrial facilities, it underpins safety systems and operational efficiency. When gravity and distance work against the water supply, booster pumps step in as the essential solution to ensure every tap delivers.
This post will explore the critical role of booster pumps in building water systems. We will cover what they are, why they are necessary, and how they work to provide a stable and efficient water supply. You will learn about different types of systems, their benefits, and what to consider when choosing one for your building.
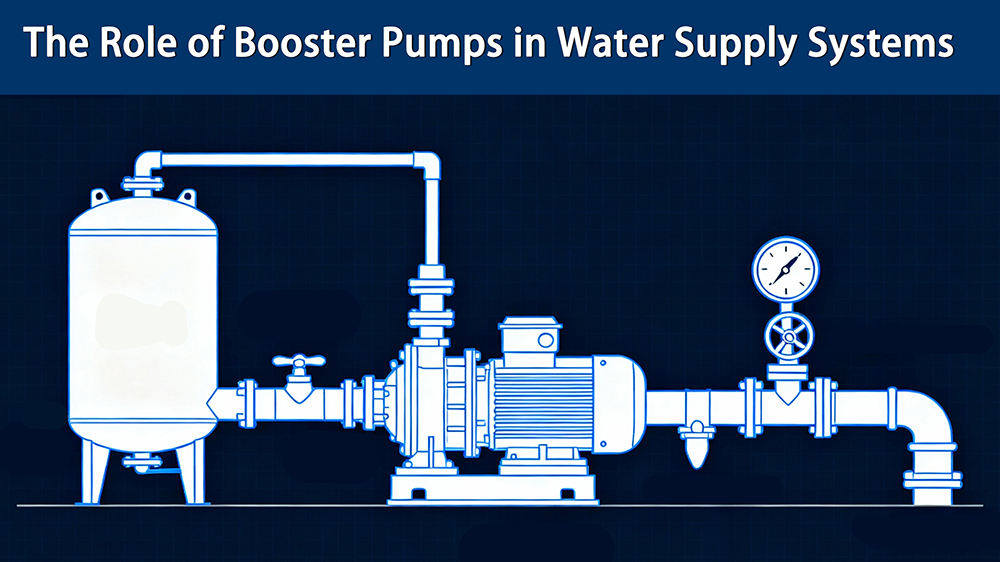
A booster pump is a device that increases the pressure of water moving through a pipeline. Unlike a standard pump that might draw water from a source like a well, a booster pump takes existing flow from the main supply line and 【boosts】 its pressure to a desired level. This ensures that water reaches every part of a building, regardless of height or distance from the source.
These systems work on a simple principle: an impeller, which is a rotating component with blades, is driven by a motor. As water enters the pump, the impeller spins rapidly, adding kinetic energy to the water and forcing it out at a higher pressure.
Key components of a booster pump system include:
Motor: Powers the pump.
Impeller: The rotating part that increases water velocity and pressure.
Pressure Tank: A small storage vessel that helps maintain pressure and reduces how often the pump needs to cycle on and off.
Control System: A pressure switch or a more advanced controller that automatically starts and stops the pump based on system demand.
Many types of buildings rely on booster pumps to overcome specific water supply challenges. Without them, upper floors would experience weak flow, and systems could fail during periods of high demand.
High-Rise Buildings
In tall structures, gravity is the primary enemy of water pressure. For every 10 feet of vertical rise, water pressure drops by approximately 4.3 PSI. A booster pump system is necessary to counteract this pressure loss, ensuring that apartments and offices on the top floors have the same reliable water pressure as those on the ground floor.
Commercial and Industrial Facilities
Large commercial complexes, such as shopping malls and hotels, experience significant fluctuations in water demand. Booster pumps maintain a stable supply during peak hours, like morning rushes or busy weekends. In industrial settings, they are crucial for providing the consistent pressure required for manufacturing processes, cooling systems, and critical fire protection sprinkler systems.
Residential Systems
Even in smaller residential buildings or large single-family homes, booster pumps can make a noticeable difference. They improve the performance of showers, faucets, and water-dependent appliances like washing machines and dishwashers, providing a more comfortable and convenient living experience.
Booster pumps are integrated into a building's plumbing network, typically after the main water meter and any storage tanks. The system operates as part of a carefully designed layout to manage pressure automatically.
A typical setup involves the booster pump drawing water from the municipal supply line or a break tank. Pressure sensors installed in the pipes monitor the system's pressure. When someone opens a faucet, the pressure drops. Once it falls below a pre-set threshold, the control system activates the pump. The pump runs until the pressure is restored to the desired level, at which point the controller shuts it off. This automatic start/stop cycle ensures pressure is always available on demand.
Modern systems often use Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs). Instead of just turning on and off, a VFD adjusts the pump motor's speed in real-time to precisely match water demand. This provides perfectly constant pressure and significantly reduces energy consumption.
Booster pump systems come in various configurations, each suited for different applications and building sizes.
Single Pump Systems
Simple and cost-effective, a single pump system is ideal for small buildings or homes where water demand is relatively low and consistent. They provide a basic pressure boost but lack redundancy.
Multistage Pumps
These pumps feature multiple impellers arranged in a series. Each stage adds more pressure, making multistage pumps perfect for high-rise buildings that require a significant pressure increase (high head) to move water to the upper floors.
Variable Speed (VFD) Systems
VFD booster systems are the standard for energy efficiency and performance. By adjusting the motor speed to meet real-time demand, they prevent the pump from running at full power unnecessarily. This not only saves electricity but also reduces wear and tear on the components.
Parallel Pump Systems
For large facilities like hospitals, data centers, and expansive hotels, parallel systems are used. These setups involve two or more pumps working together. They offer redundancy—if one pump fails, another can take over. They also allow for load sharing, where multiple pumps run at partial capacity for maximum efficiency during periods of high demand.
Installing a high-quality booster pump system offers several advantages for building owners and occupants.
Consistent Water Pressure: The most immediate benefit is reliable and strong water pressure at every outlet, from the basement to the top floor.
Improved System Reliability: By maintaining steady pressure, booster pumps reduce stress on pipes and fixtures, minimizing the risk of leaks and water hammer. Parallel systems add a layer of redundancy, preventing total system failure.
Enhanced Energy Efficiency: VFD-controlled systems can reduce energy consumption by 30-50% compared to fixed-speed pumps, leading to substantial operational cost savings.
Reduced Noise and Maintenance: Modern booster sets are designed for quiet operation. Smart controls also reduce unnecessary cycling, which extends the lifespan of the pump and lowers maintenance needs.
Proper installation and regular maintenance are crucial for the long-term performance and reliability of a booster pump system.
During installation, the pump should be placed in an accessible location, often in a basement or mechanical room after the water storage tank. It's important to use vibration and noise isolation pads to prevent operational sounds from traveling through the building structure.
Routine maintenance should include:
Regular inspection of pressure sensors and control valves to ensure they are functioning correctly.
Checking the pressure tank's air charge to prevent the pump from cycling too frequently.
Ensuring the system is free of air, as trapped air can cause cavitation—a damaging phenomenon that can destroy the impeller.
Listening for unusual noises, which could indicate worn bearings or other mechanical issues.
Selecting the appropriate booster pump requires a careful assessment of the building's specific needs. Key factors to consider include:
Water Demand: Calculate the peak water demand based on the number of fixtures, units, and occupants.
Building Height: The total height the water needs to travel will determine the required pressure (head).
Materials: Look for pumps with corrosion-resistant components, such as stainless steel impellers and casings, to ensure durability and water quality.
Certifications and Efficiency: Choose pumps from reputable brands that are certified for safety and performance. Prioritize energy-saving models with VFD control to maximize long-term value.
Booster pumps are no longer just a luxury; they are a fundamental component of modern building infrastructure. They solve the inherent challenges of water distribution in structures of all sizes, ensuring comfort, safety, and efficiency. By investing in a properly designed, installed, and maintained booster pump system, building owners can guarantee a reliable water supply for years to come. As technology advances, smart booster systems will continue to play an even greater role in creating sustainable and high-performing buildings.
Address
No.17 XeDa Jimei Ind. Park, Xiqing Economic Development Area, Tianjin, China
Telephone
+86 13816508465
QUICK LINKS